
Decoding Discharge: Understanding Cervical Mucus and Fertility
By Team on 02 Mar, 2024
What is Cervical Mucus?
The Changing Nature Of Cervical Mucus
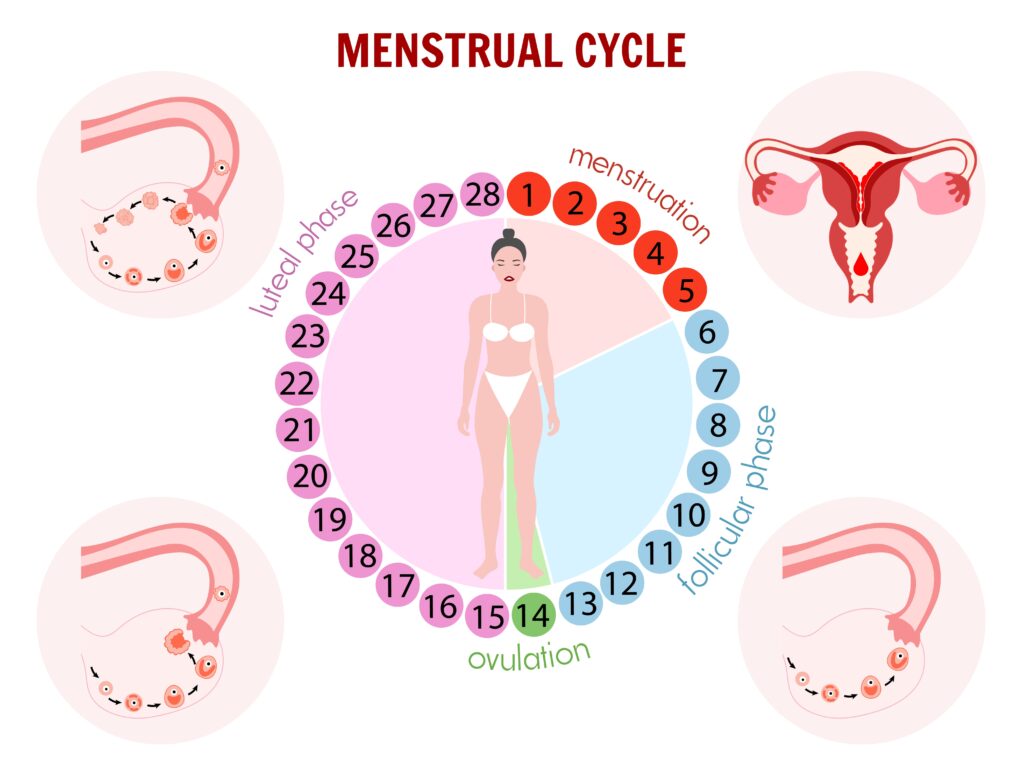
Early Follicular Phase ( Days 1-5) : Following menstruation, estrogen levels are low in the body. It results in scant, sticky, or dry cervical mucus and this thick consistency effectively blocks sperm passage.
Late Follicular Phase ( Day 6- 13) : As estrogen levels slowly rise in the body, the cervical mucus starts to thin and become cloudy or white, with a creamy texture. While still not ideal for sperm, this change indicates the body’s preparation for ovulation.
Ovulation Phase (Days 14-16): Estrogen reaches its peak just before ovulation, causing a dramatic shift in cervical mucus. It becomes clear, stretchy, and slippery, resembling raw egg white. This fertile-quality mucus allows sperm to easily swim through the cervix and reach the fallopian tubes, where fertilization can occur. This window of fertile cervical mucus typically lasts 2-3 days.
Luteal Phase (Days 17-28): After ovulation, progesterone takes the center stage. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, making it cloudy, sticky, or dry once again. This change acts as a barrier to sperm, preventing them from reaching the egg released during ovulation. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, progesterone levels drop, triggering menstruation and the start of a new cycle.
Ways to Track Cervical Mucus
- Internal Observation: After using the toilet, gently insert a clean finger into the vagina and reach near the cervix. Remove your finger and observe the consistency and texture of the mucus on it.
- External Observation: Cervical mucus can also be noticed on toilet paper or underwear.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a daily record of your observations. Use terms like “dry,” “sticky,” “creamy,” “egg white,” etc., to track the changes.
Benefits of Tracking:
- Identifying Fertile Window: By recognizing the shift to clear, stretchy cervical mucus, you can pinpoint your most fertile days, increasing the chances of conception.
- Understanding Cycle Irregularities: Changes in cervical mucus patterns can sometimes indicate hormonal imbalances or menstrual cycle irregularities.
- Natural Birth Control Method: The cervical mucus method, when combined with other fertility awareness methods like basal body temperature tracking, can be used as a natural form of birth control.
Additional Tips for Boosting Fertility
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage stress, and get enough sleep. These factors play a significant role in overall health and fertility.
- Healthy Weight: Being overweight or underweight can affect ovulation and hormonal balance.
- Pelvic Exams: Schedule regular checkups with your gynaecologist to rule out any underlying health conditions that could impact fertility.
- Preconception Vitamins: Taking folic acid and prenatal vitamins can help prepare your body for pregnancy.




